If you’re considering starting the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) to manage gastrointestinal issues like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional first. This diet focuses on consuming simple carbohydrates and unprocessed foods, which can positively impact your gut microbiome and reduce inflammation. SCD involves eating easily digestible carbohydrates while avoiding high-fiber and high-protein foods. While this diet has the potential to be beneficial, it may also restrict certain nutrients and does not meet the current recommendations set by nutrition experts. Remember, the best diet for you should be balanced and fit your lifestyle, and factors like exercise play a crucial role in overall well-being. Before embarking on any dietary changes, it’s always wise to seek guidance from a healthcare professional.

This image is property of www.verywellfit.com.
What is the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD)?
The specific carbohydrate diet, or SCD, is a dietary approach that focuses on the intake of simple carbohydrates and unprocessed foods. It is designed to favorably change the gut microbiome and reduce gut inflammation. The main principle of SCD is to eat easily digestible carbohydrates while avoiding high-fiber and high-protein foods.
Focuses on intake of simple carbohydrates and unprocessed foods
SCD emphasizes the consumption of simple carbohydrates found in fruits, non-starchy vegetables, and certain dairy products. These foods are believed to be easier for the body to digest and absorb, reducing the strain on the gastrointestinal system. Additionally, SCD promotes the consumption of unprocessed foods, eliminating additives and preservatives that may cause inflammation in the gut.
Favorably changes the gut microbiome and reduces gut inflammation
One of the key benefits of SCD is its ability to positively impact the gut microbiome. The gut is home to trillions of microorganisms that play a crucial role in digestion and overall health. SCD aims to create an environment in the gut that fosters the growth of beneficial bacteria while suppressing harmful ones. This can help reduce gut inflammation, which is often associated with gastrointestinal disorders such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Involves eating easily digestible carbohydrates
A fundamental aspect of SCD is the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates. These carbohydrates require minimal breakdown by digestive enzymes, allowing for efficient absorption in the small intestine. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with compromised digestive systems, as it reduces the risk of malabsorption and nutrient deficiencies.
Avoids high-fiber and high-protein foods
To minimize gut inflammation, SCD recommends avoiding high-fiber and high-protein foods. While fiber is generally considered beneficial for digestive health, certain types of fiber can be hard to digest and irritate the gut lining. Similarly, some high-protein foods, particularly those derived from animals, can promote inflammation in the gut. By reducing the consumption of these foods, SCD aims to alleviate symptoms and promote overall gut health.
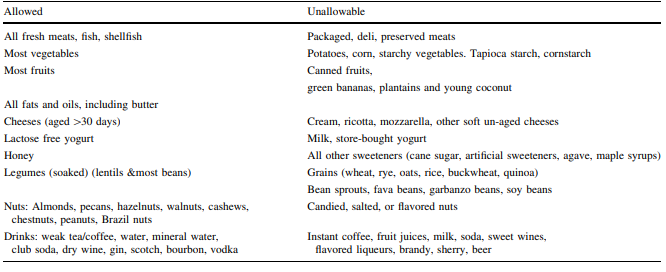
Foods allowed on the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD)
When following SCD, there is a wide range of foods that are allowed. These foods provide essential nutrients and are considered safe for individuals adhering to the diet.
Fruits
Fresh fruits are a staple of the specific carbohydrate diet. They are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, and they provide natural sugars that are easily digestible. Fruits such as bananas, apples, berries, and melons are often included in SCD meal plans.
Non-starchy vegetables
Non-starchy vegetables, such as spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, and bell peppers, are also permitted on the specific carbohydrate diet. These vegetables are low in carbohydrates and rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They provide essential nutrients while being gentle on the digestive system.
Nuts
Nuts, including almonds, walnuts, and cashews, are allowed on SCD. They are a good source of healthy fats, protein, and fiber. However, it’s important to consume them in moderation, as excessive intake can lead to digestive discomfort.
Proteins
Proteins are a vital part of the specific carbohydrate diet. Lean meats such as chicken, turkey, and fish are allowed, as they are easier to digest compared to fatty cuts of meat. Eggs and some dairy products, like natural yogurt and certain types of cheese, are also included in SCD.
Dairy products
Certain dairy products, such as natural yogurt and aged cheeses, are permitted on SCD. These products are typically lower in lactose, making them easier to digest for individuals who are lactose intolerant. It’s important to note that not all dairy products are allowed on SCD, as some may contain additives or sugars that can trigger gut inflammation.
This image is property of www.drlamcoaching.com.
Foods restricted on the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD)
While SCD allows for a wide variety of foods, there are certain food groups that are restricted or should be avoided altogether. These foods can potentially trigger gut inflammation and are not considered suitable for individuals following SCD.
Grains
Grains, including wheat, barley, rye, and oats, are restricted on the specific carbohydrate diet. These grains contain complex carbohydrates and certain types of fibers that are challenging for the digestive system to break down. Avoiding grains helps reduce the strain on the gut and minimize inflammation.
Legumes
Legumes, such as beans, lentils, peanuts, and soybeans, are also restricted on SCD. Legumes contain indigestible carbohydrates known as oligosaccharides, which can cause bloating, gas, and other digestive discomforts. By eliminating legumes from the diet, individuals following SCD may experience relief from these symptoms.
Processed proteins
Processed proteins, such as deli meats, sausages, and canned meats, should be avoided on the specific carbohydrate diet. These products often contain additives, preservatives, and high levels of sodium, which can contribute to gut inflammation. The focus of SCD is on consuming fresh, unprocessed proteins to support gut health.
Sugar
Refined sugars, including table sugar, honey, and syrups, are restricted on SCD. These sugars can rapidly spike blood sugar levels and contribute to inflammation in the gut. SCD encourages the consumption of natural sugars found in fruits, which are easily digested and less likely to cause adverse effects.
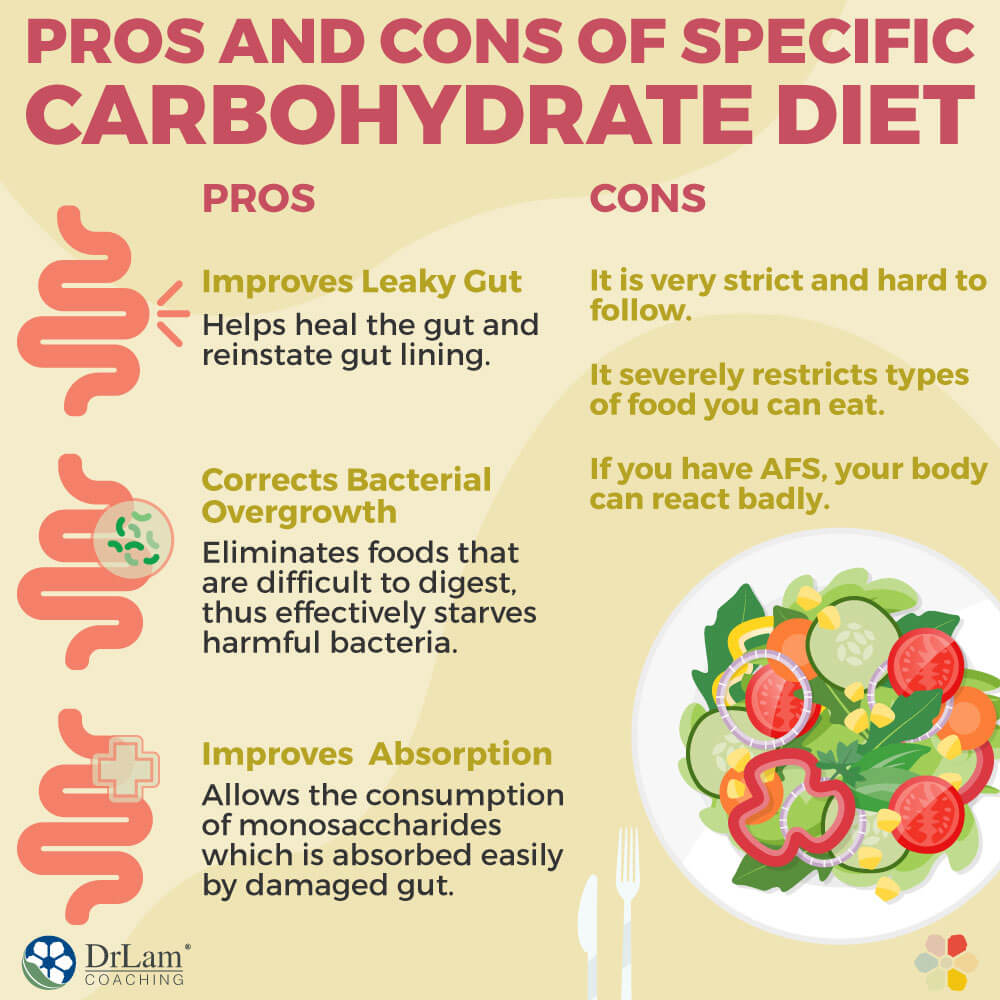
Potential benefits of the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD)
The specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) has gained attention for its potential benefits in managing gastrointestinal issues, particularly Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Management of gastrointestinal issues (e.g. Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis)
SCD has shown promise in managing symptoms and reducing inflammation in individuals with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Both of these conditions are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases that can cause persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain, and other gastrointestinal issues.
By eliminating certain complex carbohydrates and high-fiber foods, SCD aims to ease the strain on the digestive system and reduce inflammation in the gut. This can lead to a reduction in symptoms, improved quality of life, and potentially fewer flare-ups for individuals with these conditions.
While SCD may not be a cure for Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, it can be used as an adjunct therapy alongside medical treatments and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.

This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Limitations of the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD)
Although the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) has seen success in some cases, it is important to acknowledge its limitations.
Effectiveness of SCD is limited
The effectiveness of SCD in managing gastrointestinal issues may vary from person to person. While some individuals may experience significant improvements in symptoms, others may not see the same level of benefit. It is important to note that SCD is not a one-size-fits-all approach and may not be effective for everyone.
May restrict certain nutrients
SCD’s focus on eliminating certain food groups, such as grains and legumes, raises concerns about nutrient deficiencies. Grains, for example, are a good source of fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. Legumes provide plant-based protein and fiber. Excluding these foods may require careful meal planning and the inclusion of alternative nutrient sources to ensure a balanced diet.
Individuals considering SCD should work closely with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to assess their nutrient needs and develop a comprehensive plan that ensures all essential nutrients are obtained.
Importance of consulting healthcare professionals
Before embarking on the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD), it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals, such as a healthcare provider or registered dietitian, who can provide guidance and monitor your progress.
SCD should be approached under medical supervision
As SCD involves significant dietary changes and exclusion of certain food groups, it is essential to have medical supervision throughout the process. A healthcare professional can evaluate your medical history, current health status, and specific needs to determine whether SCD is suitable for you. They can provide personalized advice and monitor your progress along the way.
Consultation helps assess individual suitability for SCD
Not everyone may be suitable for SCD. Certain medical conditions, allergies, or dietary restrictions may make it challenging to follow the diet effectively. By consulting with healthcare professionals, you can assess your individual suitability for SCD and explore alternative dietary options if necessary.
Healthcare professionals provide guidance on nutrient adequacy and potential risks
One of the key benefits of consulting healthcare professionals is their expertise in assessing nutrient adequacy. They can help ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs while following SCD. They can also guide you in identifying potential risks or complications associated with the diet and provide strategies to minimize them.
They can monitor the effectiveness of SCD on specific conditions
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in monitoring the effectiveness of SCD on specific conditions, such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. Regular check-ins and follow-ups allow them to assess your progress, make necessary adjustments, and determine whether additional treatments or interventions are needed.

This image is property of www.drlamcoaching.com.
SCD as a long-term treatment, not a short-term diet
It is important to understand that the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) is not a short-term diet for weight loss, but rather a long-term treatment for gastrointestinal diseases.
SCD is not intended for weight loss
SCD focuses on improving gut health and managing gastrointestinal conditions, rather than promoting weight loss. While some individuals may experience weight changes while following SCD, the primary goal of the diet is to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
It is a treatment for gastrointestinal diseases
SCD is primarily used as a treatment for gastrointestinal diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Its potential benefits lie in reducing inflammation in the gut, improving nutrient absorption, and alleviating symptoms associated with these conditions. It should be implemented as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes medical interventions and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Requires commitment and adherence to achieve desired results
To achieve the desired results, adherence to the specific carbohydrate diet is crucial. Following the dietary guidelines strictly and making sustainable lifestyle changes are essential for long-term success. It is important to keep in mind that SCD may require adjustments over time based on individual needs and ongoing evaluations by healthcare professionals.
Considerations for the best diet
While the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) may be beneficial for individuals with certain gastrointestinal issues, it is essential to consider other factors when determining the best diet for you.
Importance of a balanced diet
While SCD focuses on eliminating certain foods, it is important not to neglect other essential nutrients. A balanced diet that includes a variety of foods from different food groups can help ensure you receive all the necessary nutrients your body needs for optimal health. Consultation with a registered dietitian can help you create a balanced meal plan that accommodates any necessary dietary restrictions.
Diet should fit individual lifestyle
The best diet is one that fits your individual lifestyle and preferences. Considerations such as cultural background, food allergies, personal taste, and accessibility to certain foods should be taken into account. It is important to find a sustainable dietary approach that you can maintain in the long term.
Exercise and lifestyle factors play a crucial role in overall well-being
While diet plays a significant role in overall health, other lifestyle factors, such as regular physical activity, stress management, and sleep, should not be overlooked. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes exercise, adequate rest, and stress reduction techniques can contribute to overall well-being in conjunction with a balanced diet.
This image is property of blog.thatcleanlife.com.
SCD and current nutrition recommendations
It is important to note that the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) does not meet the current recommendations set by nutrition experts. While SCD may have benefits for individuals with gastrointestinal issues, it should be personalized and evaluated in conjunction with the advice of healthcare professionals.
SCD does not meet the recommendations set by nutrition experts
The exclusion of certain food groups, such as grains and legumes, in SCD may result in an imbalance of nutrients and potential deficiencies if not carefully monitored. Current nutrition recommendations emphasize the importance of a varied and balanced diet that includes all essential nutrients.
May lack certain essential nutrients
SCD may limit the intake of certain essential nutrients, such as fiber, B vitamins, and minerals that are typically found in grains and legumes. It is important to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized plan that ensures all nutrient needs are met through alternative sources.
Should be personalized and evaluated in conjunction with healthcare professionals’ advice
When considering the specific carbohydrate diet, it is crucial to involve healthcare professionals in the decision-making process. They can provide personalized guidance, monitor your progress, and ensure that the diet is appropriate for your individual health needs. Collaborating with a registered dietitian who specializes in gastrointestinal health can be particularly valuable in designing an effective dietary plan.
In conclusion, the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) has gained attention for its potential benefits in managing gastrointestinal issues, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. By focusing on simple carbohydrates and unprocessed foods, SCD aims to improve gut health and reduce inflammation. However, its effectiveness may vary from person to person, and adherence to the diet may require careful nutrient planning. Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential to ensure SCD is suitable for you, monitor your progress, and address any safety or nutritional concerns. Ultimately, the best diet is one that is balanced, personalized, and fits your individual lifestyle, taking into account factors such as exercise and overall well-being. While SCD may not meet current nutrition recommendations, it can be considered as part of a comprehensive treatment plan in consultation with healthcare professionals.