You’ve probably heard about the benefits of taking supplements to boost your health and well-being. But have you ever wondered if there could be any potential drawbacks to popping those pills? In this article, we will explore the question: Can taking supplements be harmful? Whether you’re a seasoned supplement enthusiast or just curious about the topic, join us as we uncover the potential risks and provide you with valuable insights to make informed decisions about your supplement intake.

This image is property of domf5oio6qrcr.cloudfront.net.
1. Understanding Supplements
Supplements have become increasingly popular in recent years as individuals seek ways to enhance their health and well-being. These products are designed to supplement the diet and provide additional nutrients to meet specific needs. Whether it’s boosting overall health or addressing certain deficiencies, supplements offer a convenient way to support your body’s nutritional requirements. Understanding what supplements are, common types of supplements, and why people take them can help you make informed decisions about their use.
1.1 What are supplements?
Supplements are products that contain one or more dietary ingredients, such as vitamins, minerals, herbs, botanicals, amino acids, or enzymes. They are intended to be taken orally and are available in various forms, including pills, capsules, liquids, powders, and gummies. Unlike medications, supplements are not intended to treat, prevent, or cure diseases. Instead, they aim to complement or supplement the diet by providing essential nutrients that may be lacking in your daily food intake.
1.2 Common types of supplements
There is a wide range of supplements available on the market, each targeting specific nutritional needs. Some of the most common types include multivitamins, calcium, iron, omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, and herbal supplements. Multivitamins typically contain a combination of essential vitamins and minerals, while calcium supplements are often taken to support bone health. Iron supplements help address iron deficiencies, and omega-3 fatty acid supplements provide heart-healthy fats. Probiotics promote a healthy gut, and herbal supplements utilize plants and botanical extracts to support various aspects of health.
1.3 Why do people take supplements?
People take supplements for a variety of reasons. One of the primary motivations is to meet their nutritional needs. In today’s fast-paced world, it can be challenging to consume a well-rounded diet that includes all the necessary vitamins and minerals. Supplements offer a convenient way to fill any nutritional gaps and ensure your body receives adequate amounts of essential nutrients.
Another common reason for taking supplements is to address specific deficiencies. Certain individuals may have higher nutrient requirements due to factors such as age, pregnancy, or specific health conditions. Supplements can help bridge the gap and provide the necessary nutrients that may be lacking in their diet.
Additionally, many people take supplements to support their overall health and wellness. They may believe that supplements can improve energy levels, boost immune function, enhance cognitive performance, or promote healthy skin, hair, and nails. While evidence for some of these claims may be limited, individuals often rely on supplements as part of their holistic approach to health and well-being.
2. The Benefits of Supplements
Supplements offer a range of potential benefits, including meeting nutritional needs, addressing specific deficiencies, and supporting overall health and wellness.
2.1 Meeting nutritional needs
Maintaining a balanced diet is essential for optimal health, and supplements can help ensure you get the necessary nutrients. They can be particularly beneficial for individuals with dietary restrictions, such as vegetarians or vegans, who may struggle to obtain certain vitamins and minerals solely from plant-based sources. Supplements can provide an extra source of necessary nutrients, promoting overall well-being.
2.2 Addressing specific deficiencies
Certain individuals may have specific nutrient deficiencies due to various factors, such as poor absorption or increased nutrient requirements. In such cases, supplements can be particularly helpful in addressing these deficiencies. For example, iron supplements can help individuals with iron-deficiency anemia, while vitamin D supplements can benefit those with limited sun exposure or darker skin, as the body’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight is reduced.
2.3 Supporting overall health and wellness
Supplements have gained popularity for their potential to support overall health and wellness. While not a substitute for a healthy lifestyle, they can provide additional support to boost energy levels, promote immune function, and support various bodily functions. For example, omega-3 fatty acid supplements are known for their heart-healthy benefits, while probiotics can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Including supplements as part of a well-rounded approach to health can contribute to overall well-being.
This image is property of media.defense.gov.
3. The Potential Dangers of Supplements
While supplements offer potential benefits, it is crucial to be aware of the potential dangers associated with their use. It’s important to consider factors such as lack of regulation, contamination and adulteration, interactions with medications, and the potential for overdosing on certain nutrients.
3.1 Lack of regulation
One of the primary concerns with supplements is the lack of regulation. Unlike medications, supplements are not subjected to the same rigorous testing and approval processes by regulatory authorities. This means that the quality and safety of supplements can vary greatly between manufacturers. Some products may not contain the ingredients stated on the label, or they may contain contaminants that pose potential health risks.
3.2 Contamination and adulteration
Due to the lack of regulation, there have been cases where supplements have been found to be contaminated with harmful substances or adulterated with undisclosed ingredients. Contaminants can include heavy metals, such as lead or mercury, which can have detrimental effects on your health. Adulteration occurs when supplements are spiked with pharmaceutical drugs or other substances without proper disclosure, which can lead to adverse effects or interactions with medications.
3.3 Interactions with medications
Supplements can interact with medications, potentially causing adverse effects or reducing the effectiveness of the medication. For example, some supplements, such as St. John’s Wort, can interfere with the metabolism of certain drugs, including antidepressants and birth control pills. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional and disclose all supplements you are taking to ensure there are no potential interactions with your medications.
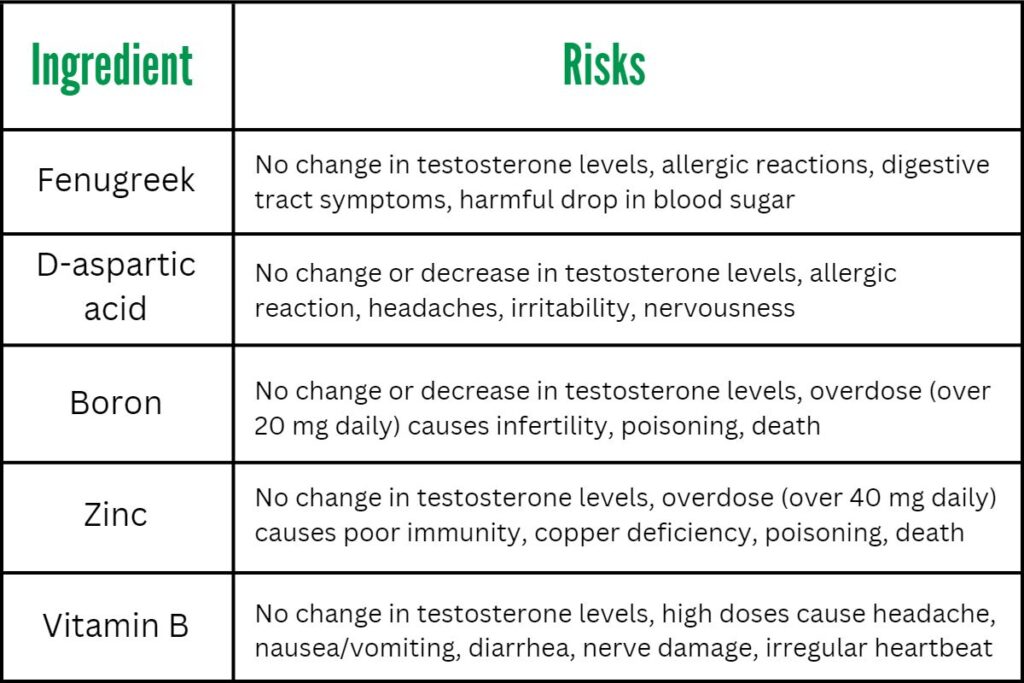
3.4 Overdosing on certain nutrients
While nutrients are necessary for good health, it is possible to overdose on certain vitamins and minerals, especially when taken in supplement form. Fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, can accumulate in the body and reach toxic levels if taken in excessive amounts. Similarly, taking high doses of minerals, such as iron, can lead to toxic effects. It is crucial to follow recommended dosages and avoid taking more than the recommended amount unless advised by a healthcare professional.
4. Risk Factors and Vulnerable Populations
Certain individuals and populations may be more at risk when it comes to supplement use. It is essential to consider these risk factors and take appropriate precautions.
4.1 Pre-existing health conditions
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as kidney disease, liver disease, or certain autoimmune disorders, may be more susceptible to the potential dangers of supplements. In some cases, supplements can exacerbate existing health issues or interfere with medications used to manage these conditions. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements if you have pre-existing health conditions.
4.2 Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals have unique nutritional needs, and supplements can play a role in meeting these needs. However, caution must be exercised, as certain supplements, such as high-dose vitamin A or herbal supplements, may be harmful to the developing fetus or nursing infant. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations regarding supplements during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
4.3 Children and adolescents
Children and adolescents have specific nutritional requirements as they go through periods of rapid growth and development. While supplements can be beneficial in certain cases, such as iron supplementation for children with iron-deficiency anemia, caution must be exercised. Children and adolescents should not take supplements without the guidance of a healthcare professional, as excess intake of certain nutrients can have adverse effects on their health.
4.4 Older adults
Older adults may have increased nutrient requirements and a higher risk of nutrient deficiencies due to factors such as reduced appetite, impaired absorption, or medication interactions. However, older adults are also more susceptible to the potential dangers of supplements, such as drug interactions or overdosing. It is crucial for older adults to consult with their healthcare professional and have their nutrient requirements assessed before starting any new supplements.

This image is property of pbs.twimg.com.
5. Common Side Effects of Supplements
While many people may benefit from supplement use, it is important to be aware of potential side effects that can occur.
5.1 Digestive issues
Digestive issues, such as nausea, diarrhea, or constipation, are common side effects of certain supplements. This can occur due to the ingredients used in the supplements or individual sensitivities. It is important to monitor your body’s reaction to supplements and consult with a healthcare professional if you experience persistent digestive issues.
5.2 Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions can occur in response to certain supplements, particularly those containing ingredients derived from allergenic sources, such as nuts, soy, or shellfish. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include hives, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms after taking a supplement, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
5.3 Nausea and vomiting
Some individuals may experience nausea or vomiting after taking certain supplements, particularly those that need to be taken on an empty stomach. If these symptoms persist or become severe, it is important to discontinue the supplement and consult with a healthcare professional.
5.4 Headaches
Headaches can occur as a side effect of certain supplements, particularly those that contain stimulants or ingredients that can affect blood flow. If you experience persistent headaches after taking a supplement, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and appropriate course of action.
6. Interactions with Medications
Supplements can interact with medications, potentially leading to adverse effects or reduced efficacy of the medication. It is crucial to be aware of these interactions and discuss them with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
6.1 Blood thinners
Certain supplements, such as fish oil or ginkgo biloba, can have blood-thinning effects. When taken together with blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin or aspirin, this can increase the risk of bleeding. It is essential to inform your healthcare professional if you are taking any supplements while on blood thinners.
6.2 Antiplatelet drugs
Supplements that have blood-thinning effects, such as garlic or ginger, can also interact with antiplatelet drugs, including clopidogrel or ticagrelor. This can increase the risk of bleeding or interfere with the antiplatelet effects of the medication. It is crucial to disclose all supplement use to your healthcare professional if you are taking antiplatelet drugs.
6.3 Antidepressants
St. John’s Wort is a popular herbal supplement used for mood support. However, it can interact with certain antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), leading to a potentially dangerous condition known as serotonin syndrome. It is vital to inform your healthcare professional if you are taking St. John’s Wort or any other supplements while on antidepressant medication.
6.4 Immunosuppressants
Supplements that have immune-boosting properties, such as echinacea or turmeric, can interact with immunosuppressant medications, reducing their effectiveness. This can increase the risk of organ rejection in individuals who have had organ transplants. It is crucial to discuss all supplement use with your healthcare professional if you are taking immunosuppressant medications.
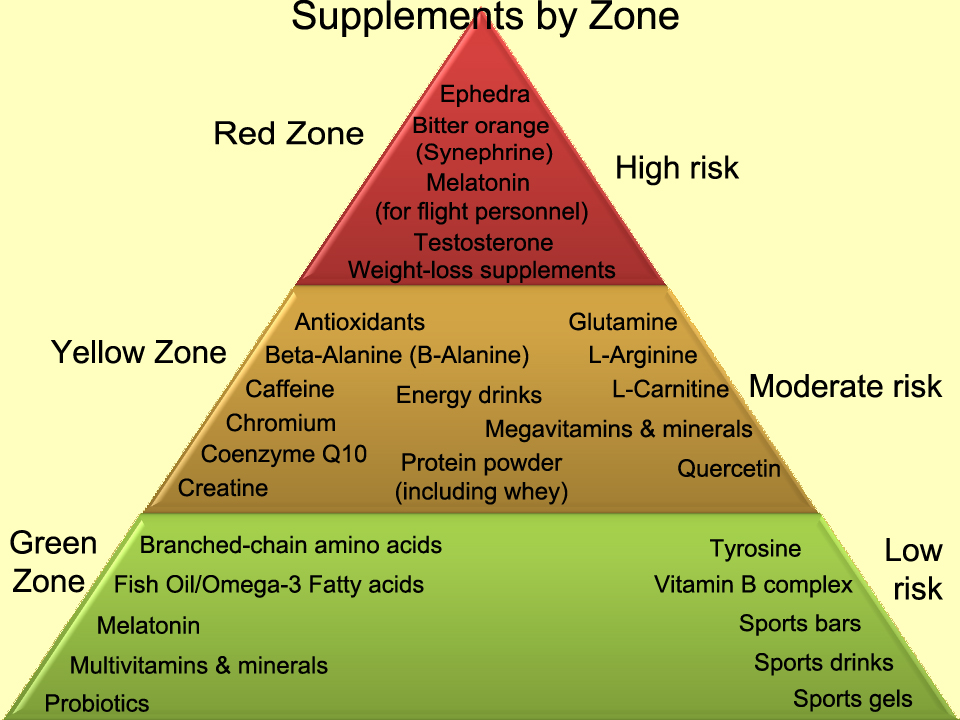
This image is property of lowtcenter.com.
7. Potential for Overdosing
While nutrients are necessary for good health, it is possible to overdose on certain vitamins, minerals, or other substances commonly found in supplements. It is important to be aware of the potential for overdosing and to follow recommended dosages.
7.1 Fat-soluble vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamins A, D, E, and K, can accumulate in the body and reach toxic levels if taken in excessive amounts. This can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, or even organ damage. It is important to follow the recommended dosages for fat-soluble vitamins and avoid taking higher doses without the guidance of a healthcare professional.
7.2 Iron and other minerals
Taking excessive amounts of minerals, such as iron, can lead to toxic effects. Overdosing on iron supplements can cause symptoms such as nausea, constipation, or even organ failure. It is crucial to follow the recommended dosages for minerals and avoid taking more than necessary.
7.3 Herbal supplements
Herbal supplements can also carry the potential for overdosing, particularly if taken in excessive amounts or for extended periods. Certain herbal supplements can have pharmacological effects and may interact with medications or have adverse effects on the body. It is important to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new herbal supplement.
7.4 Performance-enhancing substances
The use of performance-enhancing substances, such as certain sports supplements or hormonal supplements, carries a high risk of overdosing. These substances can have serious health consequences and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, if at all. It is important to prioritize your health and avoid the temptation to use these substances without proper supervision.
8. Misleading Labeling and False Claims
Another concern with supplements is the potential for misleading labeling and false claims. It is important to be vigilant and cautious when assessing the accuracy of supplement labels and health claims.
8.1 Inaccurate ingredient lists
Some supplements have been found to contain ingredients that are different from those listed on the label. This can pose a significant risk, as individuals may unknowingly consume allergens or other harmful substances. It is important to buy supplements from reputable manufacturers and look for third-party verification or certification to ensure the accuracy of ingredient lists.
8.2 Exaggerated health benefits
Supplement manufacturers may sometimes make exaggerated claims about the health benefits of their products. It is important to approach these claims with skepticism and look for scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of the supplement. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if the supplement aligns with your health goals and is safe for your specific circumstances.
8.3 Unsupported claims of safety
Supplement manufacturers may sometimes make claims about the safety of their products without sufficient evidence. It is important to remember that supplements are not regulated in the same way as medications. Just because a supplement is marketed as “natural” or “safe” does not guarantee its safety or efficacy. Always consult with a healthcare professional and prioritize your health and safety when considering supplements.

This image is property of images.everydayhealth.com.
9. Precautions and Safety Measures
To minimize the potential dangers associated with supplement use, it is important to take certain precautions and follow safety measures.
9.1 Consulting a healthcare professional
Before starting any new supplements, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or a registered dietitian. They can assess your unique nutritional needs, evaluate potential interactions with medications, and provide personalized guidance on supplement use.
9.2 Buying from reputable manufacturers
To ensure the quality and safety of supplements, it is important to purchase them from reputable manufacturers. Look for products that have been third-party tested or certified by independent organizations to ensure accuracy in labeling and the absence of contaminants.
9.3 Reading and understanding labels
Carefully read and understand the labels of supplements before purchasing or consuming them. Pay attention to the recommended dosage, ingredients, and any potential warnings or contraindications. If anything is unclear, consult with a healthcare professional or contact the manufacturer directly for clarification.
9.4 Following recommended dosages
Always follow the recommended dosages for supplements and avoid exceeding the recommended amount unless advised by a healthcare professional. Taking higher doses does not necessarily lead to better results and can increase the risk of adverse effects. Remember that supplements are intended to supplement the diet and should not replace a balanced and varied diet.
10. Conclusion
When it comes to supplements, weighing the risks and benefits is crucial. While supplements can offer a convenient way to meet nutritional needs, address deficiencies, and support overall health and wellness, they also come with potential dangers. Lack of regulation, contamination, interactions with medications, potential for overdosing, misleading labeling, and false claims are all factors that must be considered. By making informed choices, consulting with healthcare professionals, and prioritizing a balanced diet, you can navigate the world of supplements safely and effectively. Remember, your health and well-being should always be the top priority.