In this article, you will explore the fascinating realm of mental health prevention and discover the various types of techniques used to safeguard our well-being. With an increasing awareness of mental health issues in today’s society, it is crucial to understand how prevention strategies can play a vital role in maintaining our mental well-being. From primary prevention to tertiary prevention, you will delve into the different approaches aimed at promoting mental wellness and preventing the onset and escalation of mental health disorders. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey and uncover the diverse array of prevention methods in mental health. Mental health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and it is important to prioritize prevention strategies in order to promote positive mental health outcomes. There are several different types of prevention in mental health, each with its own unique goals and strategies. These types of prevention can be classified into five categories: primary prevention, secondary prevention, tertiary prevention, universal prevention, selective prevention, and indicated prevention. Additionally, there are several important approaches and initiatives that support mental health prevention efforts, such as advocacy and awareness campaigns, community-based interventions, workplace mental health programs, and research and innovation.
This image is property of youth.gov.
Primary Prevention
Education and Awareness Programs
Education and awareness programs play a crucial role in primary prevention efforts. These programs aim to promote mental health literacy and reduce stigma surrounding mental health issues. By providing information on mental health disorders, their causes, and available resources, education and awareness programs empower individuals to better understand their own mental health and that of others. These programs often occur in various settings, including schools, workplaces, and community centers, and can include workshops, presentations, and informational campaigns.
Promotion of Mental Well-being
Promoting mental well-being is another important aspect of primary prevention. This involves strategies that focus on enhancing protective factors and reducing risk factors for mental health problems. Examples of promotion activities include fostering positive relationships, building resilience and coping skills, encouraging healthy lifestyle choices, and promoting self-care practices. By proactively engaging in these activities, individuals can strengthen their mental health and develop resources that support long-term well-being.
Creating Supportive Environments
Creating supportive environments is essential for primary prevention efforts. This includes developing communities, workplaces, and educational settings that are conducive to positive mental health outcomes. Supportive environments prioritize mental health promotion and provide resources and policies that foster well-being. This can include initiatives such as implementing flexible work policies, promoting work-life balance, and creating inclusive and supportive educational environments.
Addressing Social Determinants
Addressing social determinants is another key component of primary prevention efforts. Social determinants of mental health are the social, economic, and environmental factors that influence mental well-being. These factors can include poverty, discrimination, unemployment, and lack of access to healthcare services. By addressing these determinants, communities can reduce the risk of mental health problems and promote better overall mental health outcomes for individuals.
Secondary Prevention
Early Intervention Programs
Early intervention programs are crucial for identifying and addressing mental health problems at an early stage. These programs aim to provide support and treatment to individuals who may be experiencing emerging mental health issues. By intervening early, these programs can prevent the escalation of mental health problems and improve outcomes for individuals. Early intervention programs can include targeted assessments, individual or group therapy, and referral to specialized services.
Screening and Assessment
Screening and assessment are essential components of secondary prevention efforts. Regular screening and assessment can help identify individuals who may be at risk of developing mental health problems or who are already experiencing symptoms. Mental health professionals use standardized tools and assessments to gather information and determine the appropriate course of action. Screening and assessment can take place in various settings, including healthcare facilities, schools, and workplaces.
Brief Intervention Strategies
Brief intervention strategies are designed to provide immediate support and assistance to individuals who may be experiencing mental health problems. These interventions are typically short-term and aim to address immediate needs and concerns. Brief intervention strategies can include counseling sessions, crisis support, and referrals to appropriate resources. By providing timely assistance, these strategies can prevent the progression of mental health problems and support individuals in their recovery.
Crisis Hotlines and Helplines
Crisis hotlines and helplines are vital resources in mental health prevention efforts. These services provide immediate support and assistance to individuals in crisis or who are experiencing a mental health emergency. By offering a confidential and accessible platform for individuals to seek help, crisis hotlines and helplines can potentially prevent self-harm, suicide, or the exacerbation of mental health symptoms. Trained professionals or volunteers staff these services and can offer guidance, reassurance, and referrals to further support.

This image is property of press.rebus.community.
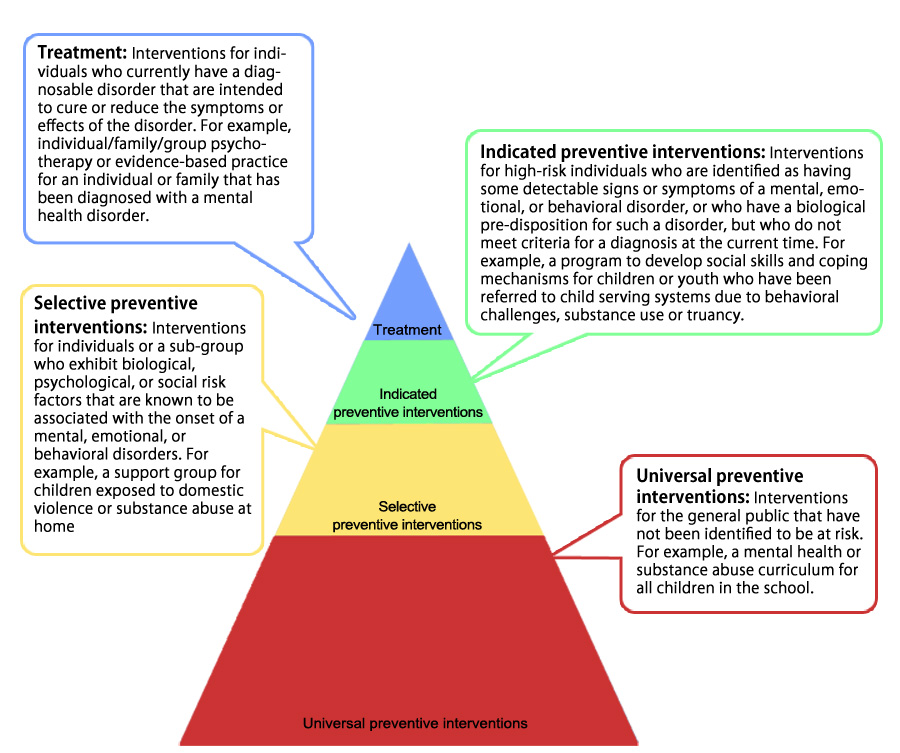
Tertiary Prevention
Treatment and Rehabilitation
Tertiary prevention focuses on providing treatment and rehabilitation services to individuals who have already experienced mental health problems. These services aim to prevent the recurrence or worsening of symptoms and support individuals in their recovery journey. Treatment and rehabilitation can include a range of modalities, such as psychotherapy, medication management, support groups, and hospitalization when necessary. By providing comprehensive care and ongoing support, tertiary prevention helps individuals regain and maintain their mental well-being.
Psychosocial Support Services
Psychosocial support services are an integral part of tertiary prevention efforts. These services focus on providing emotional and social support to individuals who have experienced mental health problems. Psychosocial support can include counseling, peer support groups, vocational training, and assistance with social integration. By addressing the social and emotional aspects of recovery, these services help individuals rebuild their lives and reduce the risk of relapse.
Case Management and Care Coordination
Case management and care coordination are crucial in supporting individuals in their recovery from mental health problems. These services involve a collaborative approach, where professionals assist individuals in navigating the mental health system, accessing necessary resources, and coordinating care across different providers and support networks. Case managers ensure that individuals receive the appropriate services and support tailored to their specific needs, thereby strengthening their recovery outcomes.
Relapse Prevention Programs
Relapse prevention programs are designed to support individuals who have experienced mental health problems in maintaining their progress and preventing future episodes. These programs include strategies to identify early warning signs, develop coping skills, cultivate healthy lifestyle choices, and build a strong support network. Relapse prevention programs promote individuals’ self-management capabilities and equip them with the tools necessary to navigate potential challenges they may encounter in their recovery journey.
Universal Prevention
Health Promotion
Health promotion initiatives play a vital role in universal prevention efforts for mental health. These initiatives focus on promoting overall well-being and reducing risk factors that contribute to poor mental health outcomes. Health promotion strategies can include awareness campaigns, educational programs, and policies that prioritize mental well-being in various settings. By integrating mental health into broader health promotion efforts, individuals and communities are better equipped to prevent mental health problems and maintain optimal well-being.
Mental Health Promotion in Schools
Mental health promotion within schools is a valuable universal prevention strategy. Schools are an ideal setting to promote positive mental health and equip students with the skills and knowledge necessary to navigate their emotional and social well-being. Schools can implement mental health curriculum, provide access to student support services, and foster a safe and supportive school environment. By prioritizing mental health promotion in schools, educators and students alike can develop resilient and healthy practices that contribute to long-term well-being.
Community-Based Programs
Community-based programs are crucial for universal prevention efforts. These programs are designed to engage individuals and communities in mental health promotion activities and provide accessible resources and support. Community-based programs can include wellness workshops, support groups, community events, and outreach initiatives. By involving diverse community members in mental health prevention efforts, these programs foster social connectedness and create supportive environments that promote positive mental health outcomes.
Policies and Legislation
Policies and legislation play a pivotal role in universal prevention efforts for mental health. Governments, organizations, and institutions have the power to implement policies and regulations that prioritize mental health promotion and protect individuals from risk factors. Policies can focus on areas such as healthcare accessibility, workplace mental health support, education curricula, and public awareness campaigns. By enacting supportive policies and legislation, society can create a foundation for mental health prevention and ensure that these efforts are sustained and prioritized.

This image is property of mnpsp.org.
Selective Prevention
Targeted Programs for High-Risk Groups
Selective prevention strategies target individuals or groups who may be at higher risk of developing mental health problems. These programs aim to address specific vulnerabilities and risk factors associated with certain populations. Examples of targeted programs include mental health interventions for individuals experiencing homelessness, substance abuse prevention programs for at-risk youth, and support groups for individuals who have experienced trauma. By tailoring prevention efforts to the unique needs of specific populations, selective prevention strategies can effectively reduce the risk and impact of mental health problems.
Family-Based Interventions
Family-based interventions are valuable in selective prevention efforts. These interventions recognize the significant impact of family dynamics on individual mental health outcomes. Family-based interventions aim to strengthen family relationships, improve communication, and enhance coping skills within the family unit. By addressing potential family stressors and providing support and education to families, these interventions can reduce the risk of mental health problems and promote healthier family functioning.
Screening and Early Detection
Screening and early detection are vital components of selective prevention strategies. Early identification of individuals who may be at risk allows for timely intervention and support. With early detection, mental health professionals can provide appropriate assessments, referrals, and interventions that assist individuals in managing their mental health. Screening and early detection can occur in various settings, such as primary care clinics, schools, workplaces, and community centers.
Skills Training Programs
Skills training programs are beneficial in selective prevention efforts, particularly for individuals who may be at elevated risk of developing mental health problems due to limited coping skills or resilience. These programs offer targeted interventions to develop specific skills, such as stress management, emotion regulation, and problem-solving. Skills training programs provide individuals with the tools necessary to effectively navigate challenging situations and build resilience against risk factors for mental health problems.
Indicated Prevention
Early Identification of At-Risk Individuals
Early identification of at-risk individuals is a critical component of indicated prevention efforts. Mental health professionals and other stakeholders must be vigilant in recognizing signs and symptoms of mental health distress. By identifying individuals at an early stage, appropriate interventions and supports can be provided promptly, potentially preventing the onset of a full-blown mental health crisis.
Referral to Specialized Services
Referral to specialized services is crucial in indicated prevention efforts. Mental health professionals play a key role in ensuring that individuals receive the appropriate level of care and support. Depending on the severity and complexity of the mental health problem, referrals may be made to psychiatrists, psychologists, social workers, or other specialists in mental health. Referral to specialized services ensures that individuals have access to the specific interventions and treatments required for their mental health needs.
Psychotherapy and Counseling
Psychotherapy and counseling are essential components of indicated prevention efforts. These interventions aim to provide individuals with evidence-based therapeutic approaches that address their specific mental health concerns. Psychotherapy and counseling can occur in various formats, including individual sessions, group therapy, and family therapy. These interventions support individuals in understanding and managing their mental health symptoms, building coping skills, and facilitating recovery.
Medication Management
Medication management is a critical aspect of indicated prevention efforts, particularly for individuals with severe or chronic mental health conditions. Psychiatrists or other healthcare providers specializing in mental health play a pivotal role in prescribing appropriate medications and monitoring their effectiveness. Medication management aims to alleviate symptoms, stabilize individuals’ mental health, and support recovery. Combined with other therapeutic interventions, medication management can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with mental health problems.

This image is property of image.slidesharecdn.com.
Advocacy and Awareness Campaigns
Stigma Reduction Initiatives
Stigma reduction initiatives are crucial in mental health prevention efforts. Stigma surrounding mental health can create barriers to seeking help and can perpetuate discrimination and marginalization. Stigma reduction initiatives aim to challenge misconceptions, educate the public about mental health, and promote empathy and acceptance. These initiatives can include public campaigns, community events, and interactive workshops that engage individuals in conversations about mental health, ultimately creating a more supportive and inclusive society.
Public Education Campaigns
Public education campaigns play a critical role in raising awareness about mental health and promoting prevention strategies. These campaigns aim to provide accurate and accessible information to the public, addressing common misconceptions and promoting positive mental health practices. Public education campaigns can be delivered through various channels, including social media, television advertisements, and community outreach initiatives. By equipping individuals with knowledge and resources, public education campaigns empower individuals to prioritize their mental health and seek appropriate support when needed.
Media Engagement and Messaging
Media engagement and messaging are powerful tools in mental health prevention efforts. The media has a significant influence on public perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors surrounding mental health. Engaging with media outlets to ensure accurate and responsible reporting on mental health is crucial. Additionally, promoting positive and stigma-free portrayals of mental health in movies, television shows, and other forms of media can help reduce stigma and create a more supportive environment for individuals with mental health problems.
Engaging with Policy Makers
Engaging with policy makers is an essential advocacy strategy in mental health prevention. By working with legislators, advocates can help shape policies and legislation that prioritize mental health promotion and prevention efforts. Raising awareness about the importance of mental health and presenting evidence-based strategies to policy makers is crucial in influencing change and garnering support. By engaging with policy makers, advocates can enact systemic changes that positively impact mental health outcomes at a societal level.
Community-Based Interventions
Community Mental Health Centers
Community mental health centers are essential components of community-based interventions in mental health prevention. These centers provide a range of mental health services, including assessments, counseling, and psychiatric care, to individuals in their communities. Community mental health centers often operate on a sliding fee scale and offer services to individuals of all ages and backgrounds. By making mental health services accessible and available in local communities, these centers contribute to improved mental health outcomes and prevention efforts.
Peer Support Programs
Peer support programs play a crucial role in community-based interventions and mental health prevention. Peer support refers to individuals with lived experience of mental health problems providing support, encouragement, and understanding to others going through similar struggles. Peer support programs can be formal or informal and may include support groups, mentoring programs, and online communities. These programs offer individuals a sense of connection and belonging, fostering resilience and promoting overall mental health and well-being.
Nonprofit Organizations
Nonprofit organizations play a significant role in community-based interventions for mental health prevention. These organizations often focus on specific mental health concerns or populations and provide a wide range of services, such as counseling, education, advocacy, and resource referrals. Nonprofit organizations also play a key role in raising awareness about mental health, reducing stigma, and advocating for policy changes. By providing community-based support and resources, nonprofit organizations contribute to the overall prevention efforts in mental health.
Collaborative Partnerships
Collaborative partnerships are crucial in community-based interventions for mental health prevention. By forming partnerships with various stakeholders, such as healthcare providers, educational institutions, community organizations, and law enforcement, a comprehensive approach to mental health prevention can be achieved. Collaborative partnerships foster information sharing, resource coordination, and the development of coordinated strategies and interventions. By leveraging collective expertise and resources, collaborative partnerships maximize the impact of mental health prevention efforts in the community.

This image is property of 1.bp.blogspot.com.
Workplace Mental Health Programs
Mental Health Policies and Guidelines
Workplace mental health programs begin with the establishment of mental health policies and guidelines. These policies outline expectations and commitments from employers regarding mental health support within the workplace. Mental health policies emphasize the importance of recognizing and addressing mental health issues, promoting a supportive and inclusive work environment, and providing access to necessary resources. By implementing mental health policies, employers prioritize the well-being of their employees and contribute to prevention efforts.
Employee Assistance Programs
Employee assistance programs (EAPs) play a vital role in workplace mental health programs. EAPs provide confidential counseling services, resources, and referral support to employees facing personal or work-related challenges, including mental health problems. These programs offer a safe and accessible space for employees to seek support without fear of judgment or negative consequences. By addressing mental health concerns early, EAPs can prevent problems from escalating and support employees in their recovery journey.
Training and Education
Training and education are essential components of workplace mental health programs. By providing employees and managers with the necessary knowledge and skills, workplaces can foster a culture of mental health support. Training and education can include awareness sessions, workshops on stress management and resilience, and skills-building programs. By equipping employees and managers with the tools to recognize and respond to mental health concerns, training and education contribute to prevention efforts and create supportive work environments.
Wellness Initiatives
Wellness initiatives are a valuable aspect of workplace mental health programs. These initiatives focus on promoting employee well-being through various activities and resources. Wellness initiatives can include fitness programs, mindfulness sessions, lunchtime activities, and access to mental health resources and tools. By integrating wellness initiatives into the workplace, employers promote healthy lifestyles, stress reduction, and positive mental health practices. By supporting employees in their overall well-being, workplaces contribute to prevention efforts in mental health.
Research and Innovation
Development of New Interventions
Research and innovation play a critical role in advancing mental health prevention efforts. By continuously developing new interventions, researchers can address gaps in current prevention strategies and improve outcomes for individuals. Research can help identify new risk factors for mental health problems, offer insight into effective prevention strategies, and evaluate the impact of existing interventions. By investing in research and innovation, the field of mental health prevention can continuously evolve and develop evidence-based practices.
Evidence-Based Practices
Adopting evidence-based practices is crucial in mental health prevention efforts. Evidence-based practices refer to interventions and strategies that have been rigorously evaluated and proven to be effective through research studies. By implementing evidence-based practices, mental health professionals and organizations can ensure that interventions are based on sound scientific evidence and are more likely to achieve positive outcomes. Evidence-based practices provide a foundation for prevention efforts and increase the likelihood of success.
Implementation Science
Implementation science plays a vital role in translating research findings into real-world practice. It focuses on understanding the barriers and facilitators of implementing evidence-based practices in various settings. By applying implementation science principles, organizations can effectively integrate evidence-based prevention strategies into routine practice. Implementation science helps ensure that interventions are delivered with fidelity and reach their intended target population, ultimately contributing to the overall effectiveness of mental health prevention efforts.
Technology and Mental Health
Technology has the potential to greatly enhance mental health prevention efforts. From online platforms and mobile applications to virtual reality and remote monitoring, technology offers innovative solutions that can reach individuals in different settings. Technology can provide accessible and convenient mental health resources, increase reach and scalability of interventions, and facilitate data collection and analysis. By harnessing the power of technology, mental health prevention can be more proactive, personalized, and responsive to individuals’ unique needs.
In conclusion, mental health prevention encompasses various strategies and initiatives aimed at promoting positive mental well-being, addressing risk factors, and providing timely support and intervention. From primary prevention to tertiary prevention, a comprehensive approach is necessary to achieve optimal mental health outcomes. By investing in education and awareness programs, promoting mental well-being, creating supportive environments, and addressing social determinants, individuals and communities can take proactive steps to prevent mental health problems. Additionally, targeted interventions, early identification, access to specialized services, and skill-building programs are vital in preventing the escalation and recurrence of mental health problems. Advocacy and awareness campaigns, community-based interventions, workplace mental health programs, and research and innovation further support mental health prevention efforts. By working collaboratively, investing in evidence-based practices, and utilizing technology, mental health prevention can become a priority across all levels of society, leading to improved mental health outcomes for all.
