In your quest for optimal health, you may have wondered: What is the most common dietary supplement? As we become more conscious of our well-being, dietary supplements have become increasingly popular. From multivitamins to protein powders, the options seem endless. But amidst this sea of choices, there is one supplement that stands out as the most commonly consumed. Join us on a journey to discover the answer and unlock the secrets to boosting your health.
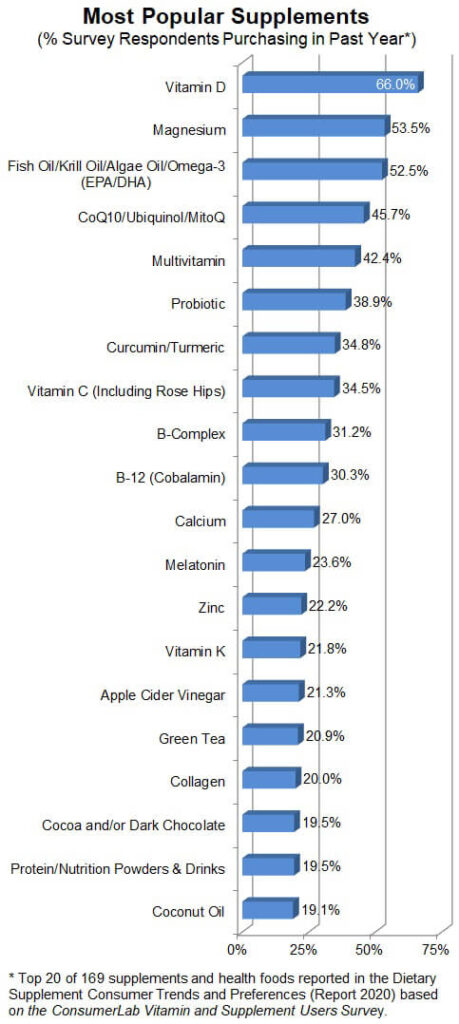
This image is property of cdn.consumerlab.com.
Vitamins
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is one of the most well-known and widely used vitamins. It is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect your body against damage from free radicals, which can lead to chronic diseases like heart disease, cancer, and aging. Vitamin C also plays a crucial role in the production of collagen, a protein that helps maintain the health of your skin, teeth, and bones. Additionally, this vitamin supports the immune system, helping you fight off illnesses and infections. Some natural sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and kiwi.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is unique because our bodies can produce it when our skin is exposed to sunlight. However, many people have insufficient levels of this vitamin due to limited sun exposure, living in areas with less sunlight, or using sunscreen. Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, which is crucial for strong and healthy bones. It also helps regulate the immune system and plays a role in reducing inflammation. Good dietary sources of vitamin D include fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is vital for the production of red blood cells and the proper functioning of the nervous system. It also plays a crucial role in DNA synthesis and maintaining healthy brain function. Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Vegetarians and vegans are at a higher risk of deficiency, as plant-based foods do not naturally contain vitamin B12. However, fortified plant-based products like certain cereals and nutritional yeast can be good sources for those following a plant-based diet.
Multivitamins
Multivitamins are popular dietary supplements that contain a combination of vitamins and minerals. They are often used to ensure adequate nutrient intake, especially for individuals who may not have a balanced diet. Multivitamins can be beneficial for people with specific dietary restrictions or those who are unable to meet their nutritional needs through food alone. However, it’s important to note that multivitamins should not replace a healthy and varied diet. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a multivitamin regimen to ensure you’re choosing the right product for your specific needs.
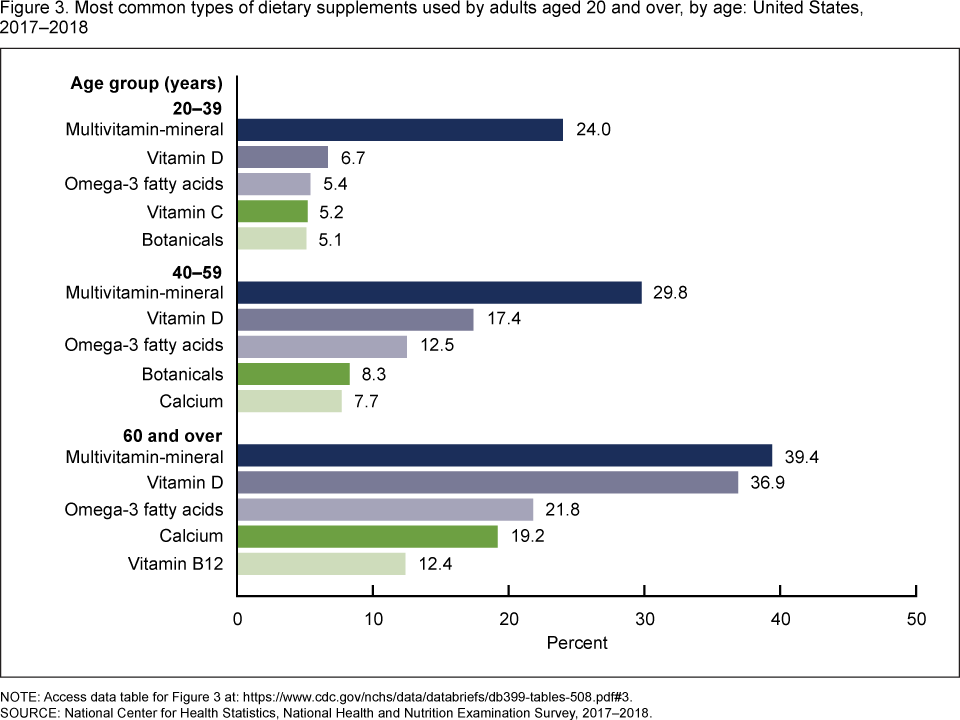
This image is property of www.cdc.gov.
Minerals
Calcium
Calcium is a vital mineral for the growth and maintenance of strong bones and teeth. It also plays a crucial role in muscle contraction, nerve function, and blood clotting. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are well-known sources of calcium. However, there are also plant-based options such as fortified plant milk, tofu, and leafy green vegetables like kale and broccoli. If you’re unable to meet your calcium needs through diet alone, calcium supplements may be recommended by your healthcare provider.
Iron
Iron is an essential mineral that is responsible for transporting oxygen throughout your body and ensuring the proper functioning of your cells. Iron deficiency is a common condition, especially among women of reproductive age and individuals with a vegetarian or vegan diet. Severe iron deficiency can lead to anemia, characterized by fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Iron-rich foods include lean meats, poultry, seafood, beans, and leafy green vegetables. Iron supplements may be prescribed by a healthcare professional for individuals with diagnosed iron deficiency or anemia.
Magnesium
Magnesium plays a crucial role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. It helps support healthy bone formation, nerve function, muscle relaxation, and blood pressure regulation. Good dietary sources of magnesium include whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, and green leafy vegetables. However, some individuals, such as those with gastrointestinal disorders or certain medications, may have difficulty absorbing magnesium from food alone. In such cases, magnesium supplements may be recommended to ensure adequate intake.
Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that is involved in multiple bodily functions, including immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. It also plays a role in taste perception and the health of your skin and eyes. Dietary sources of zinc include meat, shellfish, legumes, nuts, and seeds. In certain cases, such as zinc deficiency or increased zinc needs due to illness or pregnancy, zinc supplements may be recommended by a healthcare professional.
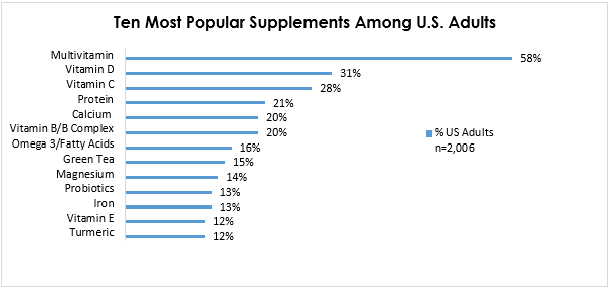
This image is property of www.crnusa.org.
Fish Oil
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Fish oil is a popular dietary supplement rich in omega-3 fatty acids, namely docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that our bodies cannot produce and must be obtained through diet or supplements. They are known for their numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation, supporting heart health, and promoting brain function. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent natural sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
EPA and DHA
EPA and DHA are two types of omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil. EPA is especially beneficial for reducing inflammation, which can help alleviate symptoms of chronic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. DHA is important for brain health and development, particularly during pregnancy and early childhood. Both EPA and DHA have been shown to support heart health by reducing the risk of heart disease and improving overall cardiovascular function.
Health benefits
Fish oil supplements have been extensively studied for their health benefits. They are known to support heart health by reducing triglyceride levels, decreasing blood pressure, and preventing the formation of blood clots. Omega-3 fatty acids also have potential benefits for mental health, as studies suggest they may help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Additionally, fish oil supplements may have anti-inflammatory effects, which can be beneficial for individuals with chronic inflammation-related conditions.

This image is property of www.crnusa.org.
