Are you a night shift worker? If so, you may have wondered about the most common health problem that affects individuals working during the darkness of night. Your curiosity is valid, and this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive answer to this question. So sit back, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s discover what health issue plagues night shift workers the most.

This image is property of blog-assets.camelohq.com.
Shift Work Disorder (SWD)
Shift Work Disorder (SWD) is a specific type of circadian rhythm sleep disorder that affects individuals who work non-traditional hours, such as night shifts, rotating shifts, or early morning shifts. It is characterized by a disruption in the natural sleep-wake cycle and can result in various physical and mental health issues.
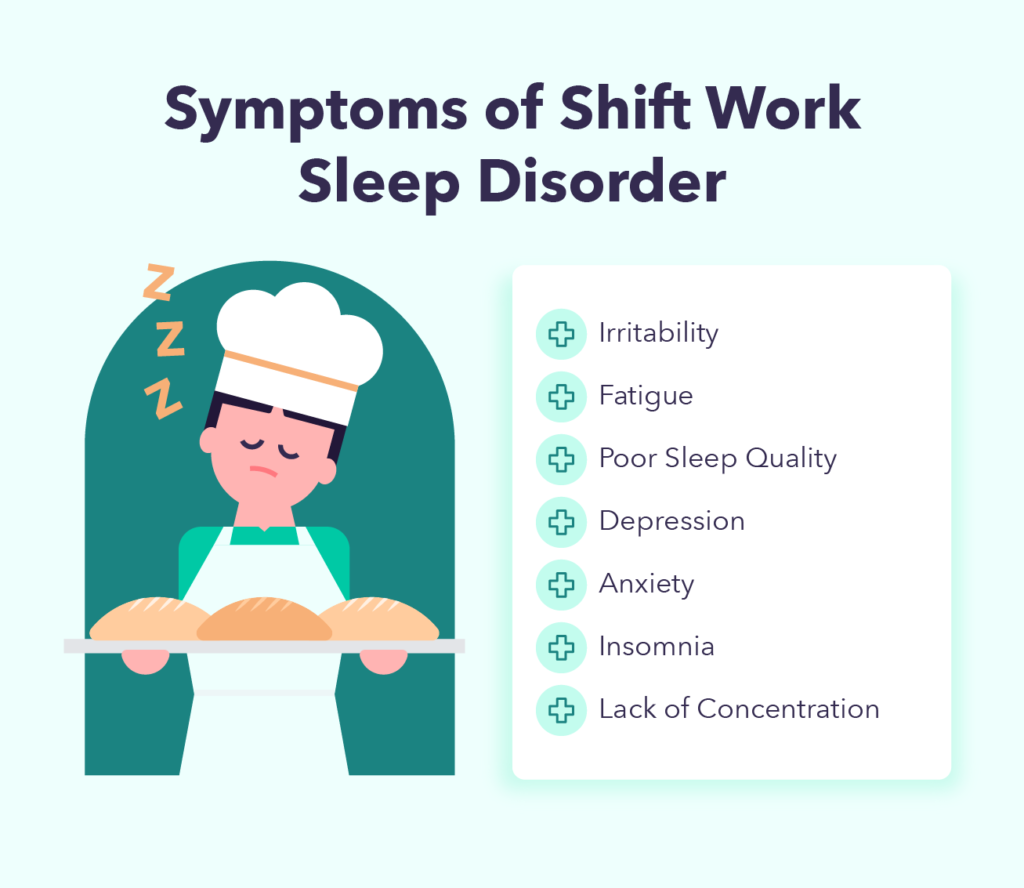
Symptoms
The symptoms of Shift Work Disorder can vary from person to person, but commonly include excessive sleepiness and difficulty staying awake during work hours, insomnia or difficulty falling asleep during off-hours, and a general feeling of fatigue or unrefreshing sleep. Other symptoms may include difficulty concentrating, irritability, and mood changes.

This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Causes
The main cause of Shift Work Disorder is the disruption to the body’s internal clock, also known as the circadian rhythm. Our bodies naturally follow a 24-hour cycle that is regulated by exposure to light and darkness. By working during the night or irregular hours, this natural cycle is disturbed, causing a misalignment between the body’s internal clock and the external environment. This misalignment can lead to various health issues associated with Shift Work Disorder.
Prevention and Treatment
Prevention and treatment of Shift Work Disorder involve several strategies. Firstly, it is important to establish a consistent sleep routine, even on days off, to help regulate the body’s internal clock. Creating a sleep-friendly environment, such as a dark and quiet bedroom, can also promote better sleep. Avoiding stimulants, such as caffeine, close to bedtime is advisable, as they can interfere with sleep quality. Additionally, incorporating regular exercise and a balanced diet into your lifestyle can help improve overall sleep and minimize the impact of Shift Work Disorder.
For those individuals who continue to experience significant difficulties, various treatment options are available. These may include medications that promote wakefulness during work hours and improve sleep during off-hours. In some cases, light therapy, where individuals are exposed to bright light during specific periods, can help regulate the body’s internal clock. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can also be beneficial, as it targets the underlying thoughts and behaviors that contribute to sleep disturbances.
This image is property of blog.mint.com.
Sleep Disorders
Apart from Shift Work Disorder, there are other common sleep disorders that night shift workers may experience. These include:
Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. Night shift workers are particularly susceptible to insomnia due to the irregular sleep-wake cycle, which can make it challenging to establish a consistent sleep routine. Chronic insomnia can lead to daytime fatigue, mood disturbances, and reduced overall well-being.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a condition in which an individual’s breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep. Night shift workers, especially those who work irregular hours, may be at a higher risk for sleep apnea due to the disruption of their sleep patterns. Sleep apnea can lead to excessive daytime sleepiness, poor concentration, and increased risk of cardiovascular problems.
Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. Night shift workers may experience worsened symptoms of RLS due to disrupted sleep patterns and irregular sleep-wake cycles. RLS can cause significant discomfort, leading to difficulty falling asleep and reduced quality of sleep.
Cardiovascular Issues
Night shift work has been associated with an increased risk of various cardiovascular issues. Some of the commonly reported issues include:
Hypertension
Night shift workers may be more prone to developing high blood pressure (hypertension) due to the disruption of their sleep patterns. Chronic sleep disturbances can negatively impact the cardiovascular system, leading to increased blood pressure levels. Hypertension is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) occurs when the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. Night shift workers have a higher risk of developing CAD compared to individuals who work during regular daytime hours. The disruption of the sleep-wake cycle and potential lifestyle factors, such as poor diet and lack of exercise, contribute to this increased risk.
Stroke
Night shift work has been associated with an increased risk of stroke. The disruption of the natural circadian rhythm and potential sleep disturbances can lead to changes in blood pressure and inflammation, both of which are risk factors for stroke. It is important for night shift workers to be aware of this increased risk and take steps to minimize it, such as prioritizing good sleep hygiene and managing other lifestyle factors.
This image is property of lh4.googleusercontent.com.
Digestive Problems
Night shift work can also have detrimental effects on digestive health. Some of the common digestive problems faced by night shift workers include:
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Night shift workers may be more susceptible to gastrointestinal disorders, such as acid reflux, indigestion, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The irregular eating patterns and disrupted sleep schedule can interfere with the digestive process and contribute to the development of these disorders. It is essential for night shift workers to prioritize a healthy diet, avoid eating late at night, and manage stress levels to mitigate the risk of gastrointestinal issues.
Weight Gain and Obesity
Studies have shown that night shift workers are more likely to be overweight or obese compared to individuals who work during regular daytime hours. This increased risk can be attributed to several factors, including disrupted sleep patterns, unhealthy eating habits, and lack of physical activity. Night shift workers should focus on maintaining a balanced diet, incorporating regular exercise, and managing stress to help prevent weight gain and obesity.
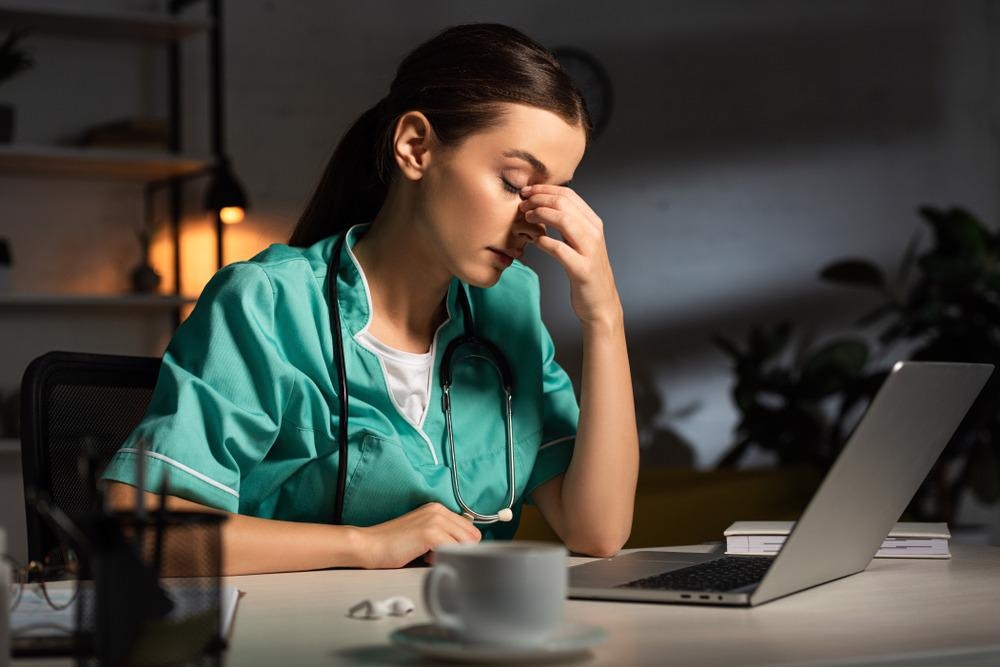
Mental Health Concerns
Working night shifts can have a significant impact on mental health. Night shift workers are at an increased risk of experiencing various mental health concerns, including:
Depression
The disruption of the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle can lead to an increased risk of depression among night shift workers. Lack of sunlight exposure and social isolation due to working non-traditional hours can further contribute to depressive symptoms. It is crucial for night shift workers to prioritize self-care, maintain social connections, and access appropriate support to reduce the risk of depression.
Anxiety
Night shift work can also contribute to feelings of anxiety and heightened stress levels. The irregular sleep schedule, potential isolation from family and friends, and the pressure to perform well during working hours can all contribute to increased anxiety. Night shift workers should develop healthy coping mechanisms, engage in relaxation techniques, and maintain a support network to manage anxiety symptoms effectively.
Stress
Working night shifts often involves dealing with high-stress situations, whether it be meeting deadlines or managing difficult circumstances. Chronic stress can negatively impact both physical and mental health. Night shift workers should focus on implementing stress management strategies, such as exercise, mindfulness practices, and adequate rest, to reduce the impact of stress on overall well-being.

This image is property of d2jx2rerrg6sh3.cloudfront.net.
Increased Risk of Accidents
Night shift work has been associated with an increased risk of accidents, both on the road and in the workplace. Some specific risks include:
Driver Fatigue
Night shift workers who commute to and from work during non-traditional hours are at a higher risk of driver fatigue. Reduced alertness and concentration due to sleep deprivation can impair driving abilities, making night shift workers more susceptible to accidents. It is essential for night shift workers to prioritize sufficient sleep and consider alternative transportation options if feeling excessively fatigued.
Workplace Accidents
Night shift workers also face an increased risk of accidents in the workplace. Fatigue, reduced vigilance, and decreased cognitive function due to sleep disturbances can impair decision-making and coordination, leading to an elevated risk of accidents or injuries. Employers should prioritize safety measures and provide appropriate training to night shift workers to minimize workplace accidents.
Impaired Cognitive Function
Night shift work can negatively impact cognitive function, leading to several issues:
Memory and Attention Problems
Lack of adequate sleep and disruption to the body’s internal clock can impair memory and attention. Night shift workers may experience difficulties in focusing, maintaining concentration, and retaining information. This can significantly impact job performance and overall productivity. Implementing strategies such as regular breaks, healthy eating, and adequate sleep can help mitigate these cognitive impairments.
Reduced Performance and Productivity
The sleep disturbances associated with night shift work can lead to reduced performance and productivity levels. Fatigue and decreased cognitive function can affect the ability to think critically, solve problems, and make decisions effectively. It is essential for night shift workers to prioritize self-care strategies, such as good sleep hygiene and stress management, to optimize performance and productivity.
Social and Lifestyle Disruptions
Night shift work can disrupt an individual’s social and personal life, leading to various challenges:
Relationship Problems
Working night shifts can create challenges in personal relationships, as night shift workers often have different schedules from their partners or family members. This can lead to reduced quality time spent together, increased feelings of isolation, and difficulties in maintaining strong relationships. Effective communication, setting aside dedicated time for loved ones, and seeking support from family and friends can help mitigate these relationship problems.
Difficulty Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
The irregular sleep schedule and potential isolation from social activities can make it challenging for night shift workers to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Poor dietary choices, lack of exercise, and increased stress levels can all contribute to an unhealthy lifestyle. Night shift workers should prioritize regular exercise, nutritious meals, and stress management techniques to maintain overall well-being.
Increased Susceptibility to Chronic Diseases
Night shift work has been linked to an increased risk of various chronic diseases:
Diabetes
Night shift workers may have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Disrupted sleep-wake cycles can affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, increasing the risk of insulin resistance and subsequent diabetes. Managing other lifestyle factors such as maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet, and regular exercise can help minimize the risk of diabetes.
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome consists of a cluster of conditions that include increased blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Night shift work has been associated with an increased likelihood of developing metabolic syndrome due to the disruption of sleep patterns and potential lifestyle factors. It is essential for night shift workers to actively manage these risk factors through a healthy lifestyle and regular health check-ups.
Cancer
Research suggests that night shift work, especially long-term and rotating night shifts, may be associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer. The disruption of the body’s circadian rhythm and potential exposure to artificial light at night can influence hormone levels and disrupt the normal cellular processes, increasing the risk of cancer development. Night shift workers should prioritize health screenings, practice good sleep hygiene, and minimize exposure to artificial light during sleep to potentially reduce this risk.
Disruptions to Circadian Rhythm
Night shift work can disrupt the body’s natural circadian rhythm, leading to various health implications:
Melatonin Imbalance
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain that helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Night shift work can disrupt the production and release of melatonin, leading to imbalances in the sleep-wake cycle. Night shift workers may experience difficulty falling asleep during the day and staying awake at night. To mitigate these imbalances, night shift workers can use techniques such as blocking out light in their bedroom during the day and using melatonin supplements under medical guidance.
Disrupted Hormonal Regulation
Night shift work can disrupt the normal regulation of hormones in the body. Hormones such as cortisol, insulin, and leptin, which play crucial roles in various bodily functions, can be affected by the disruption of the sleep-wake cycle. This can contribute to metabolic disruptions, reduced immune function, and other health issues. Night shift workers should prioritize healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise and balanced nutrition, to support hormone regulation.
In conclusion, night shift work can have a significant impact on the overall health and well-being of individuals. Shift Work Disorder, along with various other sleep disorders, cardiovascular issues, digestive problems, mental health concerns, an increased risk of accidents, impaired cognitive function, social and lifestyle disruptions, increased susceptibility to chronic diseases, and disruptions to circadian rhythm are all potential health problems that night shift workers may face. It is crucial for night shift workers and employers to be aware of these risks and take proactive measures to mitigate their impact. Prioritizing sleep hygiene, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, seeking appropriate medical support, and implementing workplace safety measures can all contribute to maintaining optimal health and well-being for night shift workers.
