In the bustling world of health and wellness, we often hear about the importance of taking supplements to support our wellbeing. However, what we might not realize is that not all supplements are meant to be taken together. In this article, you’ll discover the essential information you need to know about which supplements should not be combined. Whether you’re a newcomer to the world of supplements or a seasoned health enthusiast, these insights will help you make informed choices and maximize the benefits of your supplementation routine.
This image is property of www.singlecare.com.
Supplements That Should Not Be Taken Together
When it comes to taking supplements, it can be easy to assume that more is always better. However, this is not necessarily the case. In fact, there are certain combinations of supplements that should not be taken together as they may interfere with each other’s absorption or have adverse effects on the body. It is important to be aware of these combinations to ensure that you are getting the most out of your supplements and not putting your health at risk.
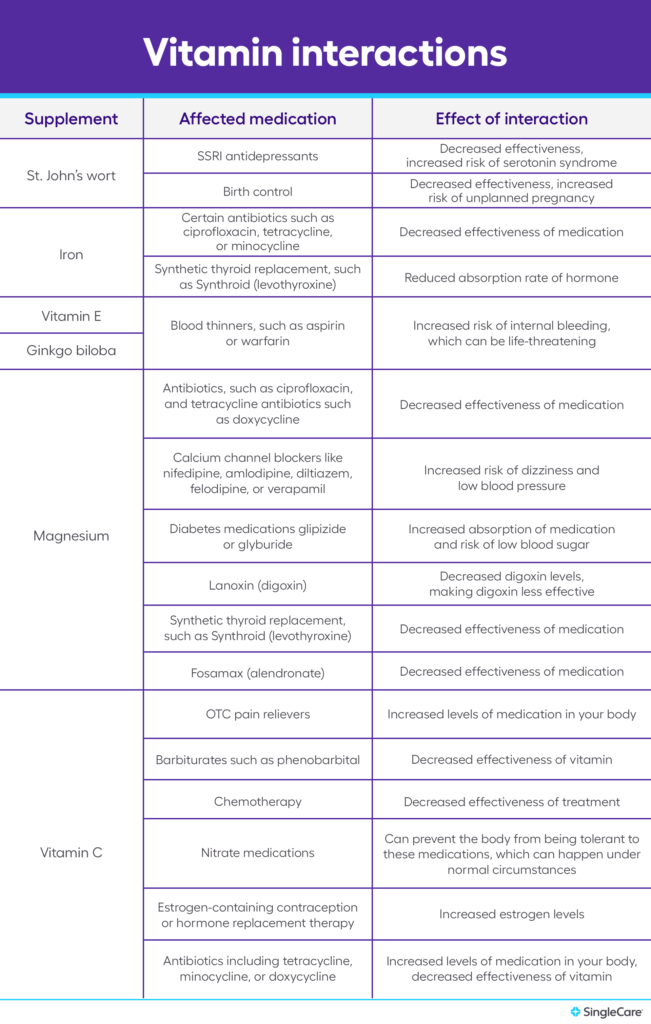
Calcium and Iron
Calcium and iron are both essential minerals that play important roles in the body. However, when taken together, they can actually reduce each other’s absorption. Calcium can interfere with the absorption of iron, making it more difficult for your body to get the iron it needs. Similarly, iron can inhibit the absorption of calcium, meaning that you may not be getting the full benefits of your calcium supplement. To avoid this interaction, it is best to take calcium and iron supplements at different times of the day.
Vitamin D and Magnesium
Vitamin D and magnesium are both essential nutrients that are involved in numerous bodily functions. However, taking these two supplements together may interfere with their absorption. Magnesium can inhibit the conversion of vitamin D into its active form, reducing its effectiveness. It is recommended to take vitamin D and magnesium supplements at different times of the day to optimize their absorption and utilization by the body.
Fish Oil and Ginkgo Biloba
Fish oil supplements are commonly consumed for their omega-3 fatty acid content, which has been linked to numerous health benefits. Ginkgo biloba, on the other hand, is a herb often used to improve cognitive function. While both supplements individually have their benefits, taking them together may lead to an increased risk of bleeding. Both fish oil and ginkgo biloba have blood-thinning effects, and when combined, this effect can be amplified. If you are taking fish oil and ginkgo biloba, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to ensure that your dosage is safe and appropriate.
St. John’s Wort and Antidepressants
St. John’s Wort is a popular herbal supplement used to alleviate symptoms of depression. However, it should not be taken together with certain antidepressant medications known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). St. John’s Wort can interfere with the way these medications work, reducing their effectiveness. Additionally, combining St. John’s Wort with SSRIs can increase the risk of a dangerous condition called serotonin syndrome. If you are currently taking antidepressants, it is important to avoid St. John’s Wort or consult with your healthcare provider before considering its use.
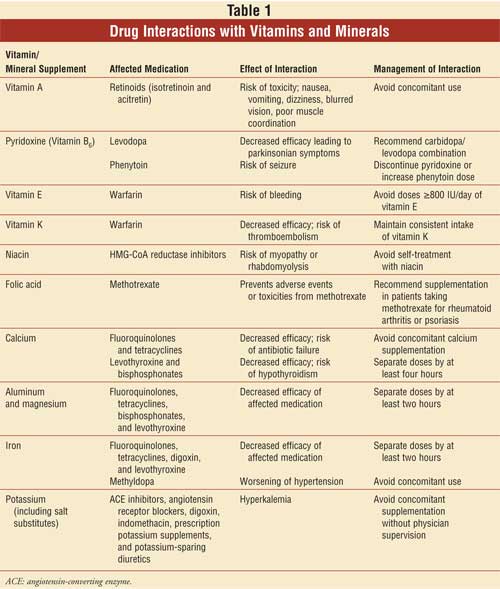
CoQ10 and Warfarin
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a naturally occurring substance found in the body and is often consumed as a supplement to support heart health. Warfarin, on the other hand, is a medication commonly prescribed as a blood thinner. When CoQ10 and warfarin are taken together, it may reduce the effectiveness of warfarin, potentially increasing the risk of blood clots. If you are taking warfarin or any other blood-thinning medication, it is advisable to speak with your healthcare provider before starting CoQ10 supplementation.
Melatonin and Warfarin
Melatonin is a hormone produced naturally by the body to regulate sleep. Many people use melatonin supplements to improve sleep quality and manage sleep disorders. However, if you are taking warfarin or any other blood-thinning medication, it is important to exercise caution when using melatonin. Melatonin has been reported to have potential interactions with warfarin, which may increase the risk of bleeding or interfere with the medication’s effectiveness. It is best to consult with your healthcare provider before combining melatonin and warfarin.
Probiotics and Antibiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support digestive health and overall well-being. Antibiotics, on the other hand, are medications used to fight bacterial infections. While probiotics are commonly recommended to restore healthy gut flora after a course of antibiotics, it is important to avoid taking them together. Antibiotics work by killing both harmful and beneficial bacteria, including probiotics. Taking probiotics and antibiotics concurrently may diminish the effectiveness of antibiotics and interfere with the healing process. It is best to wait until you have finished your antibiotic course before starting probiotics, or consult with your healthcare provider for specific recommendations.
Potassium and ACE Inhibitors
Potassium is an essential mineral involved in various bodily functions, including maintaining proper heart function. ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors are medications commonly prescribed for high blood pressure and heart conditions. While both potassium and ACE inhibitors are beneficial on their own, taking them together can raise potassium levels in the blood to potentially dangerous levels. High potassium levels, known as hyperkalemia, can lead to heart rhythm disturbances and other complications. If you are taking ACE inhibitors, it is important to monitor your potassium levels and discuss any potassium supplements or significant dietary changes with your healthcare provider.
Zinc and Copper
Zinc and copper are trace minerals that are vital for various physiological processes. While both minerals are necessary for optimal health, taking high doses of zinc supplements can interfere with copper absorption and lead to copper deficiency. Copper deficiency can result in various symptoms, including anemia and neurological issues. It is important to maintain a balance between zinc and copper intake and consider getting these minerals from dietary sources whenever possible. If you have concerns about your copper levels, consult with a healthcare provider to ensure proper supplementation.
Vitamin C and B12
Vitamin C and B12 are both essential vitamins that play important roles in the body. However, taking high doses of vitamin C may interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12. Vitamin C can convert vitamin B12 into a form that is not readily utilized by the body. This can result in vitamin B12 deficiency, which can lead to fatigue, neurological symptoms, and other complications. If you are taking vitamin C and B12 supplements, it is advisable to separate their intake or consult with a healthcare provider to ensure optimal absorption and utilization.
This image is property of www.uspharmacist.com.
Factors to Consider
In addition to being aware of specific supplement combinations to avoid, there are several factors to consider when incorporating supplements into your routine.
Timing of Supplements
The timing of supplement intake can significantly impact their effectiveness and potential interactions. Some supplements are best taken with meals to enhance absorption, while others may be more beneficial when taken on an empty stomach. It is also important to be mindful of the spacing between supplements to avoid potential conflicts.
Dosage of Supplements
The dosage of supplements can vary widely depending on individual needs and health conditions. It is important to follow recommended dosage guidelines provided by healthcare professionals or supplement manufacturers. Taking excessive amounts of certain supplements can lead to adverse effects or interactions with other medications.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Certain medical conditions or medications may affect how your body absorbs and utilizes supplements. It is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are currently taking prescription medications. They can provide personalized recommendations and monitor for any potential interactions.
Individual Sensitivities
Every individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is important to listen to your body and pay attention to any adverse reactions or side effects you may experience when taking supplements. If you notice any discomfort or unusual symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
In conclusion, while supplements can be a valuable addition to a healthy lifestyle, it is essential to be mindful of their potential interactions. Calcium and iron, vitamin D and magnesium, fish oil and ginkgo biloba, St. John’s Wort and antidepressants, CoQ10 and warfarin, melatonin and warfarin, probiotics and antibiotics, potassium and ACE inhibitors, zinc and copper, and vitamin C and B12 are some combinations to avoid. Factors such as timing of supplements, dosage, medical conditions, and individual sensitivities must be considered to ensure the safe and effective use of supplements. When in doubt, always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance on your supplement regimen. With proper knowledge and care, you can optimize the benefits of supplements while minimizing potential risks.

This image is property of www.zotezo.com.
